By Ismaila Umaru Lere
In the face of climate change, Nigeria, like many developing nations, is grappling with the dual challenges of environmental degradation and energy poverty. The reliance on fossil fuels and costly liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) has exacerbated these issues, particularly in underserved rural areas. Biomass energy, derived from organic materials, presents a sustainable and economically viable alternative for Nigeria.
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, including agricultural residues, animal waste, and forest products. It can be converted into biofuels, biogas, or directly burned for heat and electricity. Unlike fossil fuels, biomass is renewable and can contribute to a circular economy by recycling waste materials. For Nigeria, where agriculture plays a crucial role in the economy, harnessing biomass can create a sustainable energy source while addressing waste management challenges.
One of the most pressing issues in Nigeria today is energy poverty, particularly in rural areas where access to electricity and modern cooking fuels is limited. The cost of LPG can be prohibitive for many households, leading to a reliance on traditional sources like firewood and charcoal. By promoting sustainable biomass energy, Nigeria can provide affordable and accessible energy solutions.
Local biomass resources are abundant and can significantly reduce energy costs. For instance, agricultural residues such as rice husks, sugarcane bagasse, and maize stalks can be converted into bioenergy. Utilizing these resources not only lowers energy expenses but also provides additional income for farmers and rural entrepreneurs who engage in biomass production and processing.
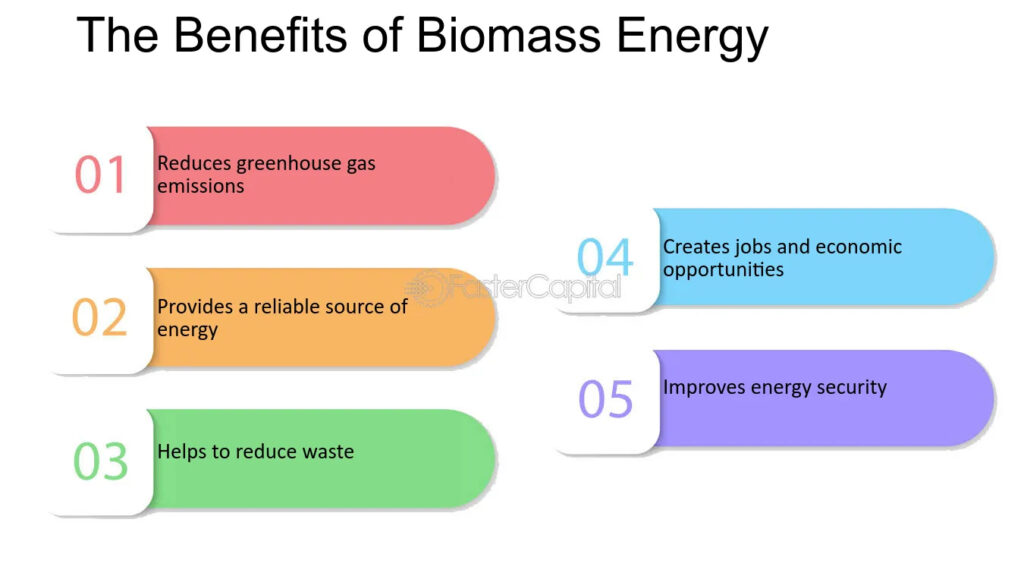
Biomass energy offers several environmental advantages that are crucial for combating climate change. First, it has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions significantly. Charcoal burning emits substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other harmful pollutants. However, when biomass is managed sustainably, the carbon released during combustion can be offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of new biomass materials.
Furthermore, biomass energy can play a vital role in waste management. By converting agricultural and organic waste into energy, Nigeria can mitigate the environmental impact of waste disposal, which often leads to methane emissions—a potent greenhouse gas. The integration of biomass into the energy mix can therefore contribute to a reduction in overall GHG emissions, helping Nigeria meet its climate commitments under international agreements.
Nigeria’s energy security is currently threatened by a heavy reliance on imported fossil fuels and the volatility of global oil prices. Biomass presents an opportunity for the country to diversify its energy portfolio and reduce dependence on external sources. By investing in local biomass production, Nigeria can enhance its energy independence, ensuring a more stable and resilient energy supply.
In rural areas, where access to electricity is sporadic, biomass energy can provide a reliable solution for cooking and heating. The establishment of community biomass facilities can empower local populations, enabling them to produce their own energy and reducing vulnerability to external shocks. This local energy production fosters resilience and self-sufficiency.
The transition to biomass energy can stimulate economic growth and create job opportunities, particularly in rural areas. The biomass supply chain—from harvesting raw materials to processing and distribution—requires manual labour, thereby creating employment in communities that struggle with high unemployment rates.
Moreover, promoting biomass enterprises can lead to the development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) focused on biomass production, processing, and technology development. These businesses can provide training and skills development for local populations, enhancing human capital and fostering innovation in the energy sector.
Integrating biomass energy production with agricultural practices can lead to sustainable land management and improved food security. Farmers can be incentivized to adopt agroforestry practices that enhance biomass production while improving soil health and biodiversity. For example, intercropping food crops with energy crops can optimize land use and provide multiple benefits.
Additionally, the use of agricultural residues for biomass energy can reduce the pressure on forest resources, helping to combat deforestation—a significant driver of climate change. By creating a closed-loop system where agricultural waste is utilized for energy, Nigeria can promote sustainable agricultural practices that contribute to both food security and environmental conservation.
While the benefits of biomass are substantial, several challenges must be addressed to realize its full potential in Nigeria. These include investment in technology for efficient biomass conversion processes which is very crucial. It involves developing biogas digesters and modern biomass cookstoves that minimize emissions and improve energy efficiency. A supportive policy environment is needed to incentivize biomass production and use. This includes access to financing for biomass projects, subsidies for sustainable practices, and regulations that promote clean energy technologies. In addition, educating communities about the benefits of biomass energy is essential for its adoption. Awareness campaigns can help change perceptions about biomass as a clean and sustainable energy source.
Indeed, biomass energy presents a promising solution for Nigeria to combat climate change while addressing energy poverty, particularly in underserved rural areas. By harnessing local biomass resources, Nigeria can reduce its reliance on expensive LPG, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainable economic development. The transition to biomass energy not only enhances energy security but also fosters job creation and sustainable agricultural practices. However, to fully realize these benefits, Nigeria must invest in technology, develop supportive policies, and raise public awareness about the advantages of biomass. Through these efforts, Nigeria can pave the way for a sustainable energy future that benefits both its people and the planet.

